This article is aimed at anyone considering dental implants or dentures and wants to know what jawbone augmentation is, when it is necessary, how the procedure works, and what risks and costs are involved. In this article, you will find answers to the following questions:
- When bone defects appear and what their main symptoms are
- How is a bone graft performed?
- When is a bone graft necessary?
- What risks are involved?
- What bone graft types are there?
- Costs of dental bone grafting
When bone defects appear and what their main symptoms are
Bone loss can be caused by old dentures, advanced gum disease, or tooth loss due to an accident. Initially, the damage is hardly noticeable because the bone loss itself does not cause severe pain. Advanced bone deficiency has the following symptoms: gum bleeding, sensitive, swollen gums, unpleasant bad breath, loose teeth, weak biting force.
How is a bone graft performed?
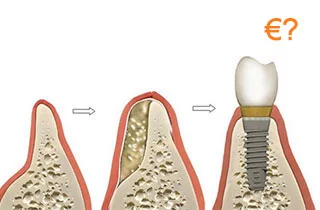
During bone augmentation, we replace the bone missing from the jaw. Before the procedure, the results of preliminary examinations (e.g., X-ray) are evaluated. Using this evaluation, the doctor can decide whether a bone augmentation procedure is necessary or not. If it is necessary, one must determine how much bone has been lost and needs to be rebuilt. Bone augmentation is a surgical treatment where the doctor makes smaller and larger incisions in the patient’s jaw. Then, the bone graft material is used for bone healing and the wound is closed.
After successful treatment, the material gradually transforms into resilient bone over several months.
The procedure consists of the following 4 steps:
- First, local anesthesia is performed. Then the surgeon opens the patient’s gingiva (gum) so that the bone can be accessed.
- During the second step, the doctor fills the area in question with a bone replacement substance.
- Last but not least, an artificial membrane is applied. It promotes the healing of the wound and accelerates recovery.
- The fourth and last step is the recovery period following the surgery; it may take 3-9 months.
When is a bone graft necessary?
As mentioned earlier, one of the main causes of bone tissue loss is missing tooth/teeth. When a tooth is lost, the mechanical stress on the bone stops, as a result of which the bone substance becomes thinner. When we want to place dental implants, it can be problematic that in a state of bone deficiency, there is not enough space for the new teeth. In these cases, bone augmentation helps, after which the implant can be placed without difficulty. Furthermore, jawbone augmentation may become necessary after the removal of a cyst or tooth root, or to stabilize loose teeth in patients with periodontal diseases. Stop bone loss in the jaw
What risks are involved?
Thanks to new technologies, the risk of complications has decreased significantly. Of course, complications can occur, as with other procedures. One possible complication is incomplete integration of the graft material with the patient’s own bone. Although this can occur, it is relatively uncommon with proper surgical planning and aftercare. With proper case selection, modern techniques, and experienced surgeons, jawbone augmentation shows a high success rate according to clinical studies. Read more about complications after bone augmentation
What bone graft types are there?
We can distinguish between the following bone graft types:
- Sinuslift
- Vertical bone graft (jaw bone lift)
- Horizontal bone grafting (jaw bone augmentation)
- The combination of the above
- Filling of bone defects
The appropriate procedure and the bone graft material depend on the patient’s condition and the goal of the operation.
In most cases, the replacement of upper molars with implants indicates the need for bone augmentation. The upper molars are so close to the sinus that their roots are often located there. Thus, an implant would also extend beyond the bone. In this case, before the implantation of the new tooth root, the implantologist performs a so-called elevation of the sinus floor (sinus lift) . In open sinus lift operations, the specialist inserts the bone graft material through the patient’s jawbone, while in a closed elevation, the procedure is performed through the area of the missing tooth.
Vertical/horizontal bone augmentation means raising/widening the jawbone through jawbone expansion. During the operation, the specialist fills the cavity with bone graft material. Filling a jawbone defect is necessary after the removal of a larger cyst.
It is common for all operations that the treated area is covered with a special membrane layer after the insertion of the bone graft material. Ossification is a slower process than gum healing. Without a membrane, the gum would occupy the bone volume, thus making the procedure pointless.
Costs of dental bone grafting
What influences the costs?
With jawbone augmentation, it is difficult to estimate the costs precisely in advance because each case is unique. The total amount is determined by the number of units of jawbone augmentation, the method, and the cost of the bone graft materials used.
The actual price of the treatment consists of:
- the cost of the surgery
- the cost of bone grafting material used
- the cost of the membrane used
during the surgery. The surgery costs depend exclusively on the method. The quantity of material consumption is always determined referring to a specific unit.
For synthetic bone graft materials, the price is calculated per gram, for membranes per piece or area. For the price of synthetic bone graft materials, the granule size is also decisive. The larger the granule, the higher the price.
Different types and costs of dental bone grafting in Hungary:
- Sinuslift: During this procedure, the dental surgeon lifts the sinuses and inserts the dental bone-graft material between the jaw bone and the sinuses. The surgical cost of a sinus lift is calculated per jaw side and the dental bone grafting costs based on the amount of necessary units to fill up the bone. The operating costs of a sinus lift are 500 Euro/jaw sides. The bone replacement material (bone of animal origin or synthetic bone) costs 100 Euro/unit.
- Vertical/horizontal bone grafting: Increasing/extending of the jaw bone by jaw bone-spreading. Here, we calculate the costs per necessary unit to ensure enough bone for an implant. One unit costs 85 Euro. For example, if two units are necessary for a position for implantation, the costs are 200 Euro in total.
Are bone grafts covered by insurance?
The costs of bone reconstruction are not covered by statutory health insurance, except in very rare cases. Private health insurance (PHI) may even cover the cost of the entire treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions about dental bone grafting costs
- Why can the costs of jaw bone grafting vary so much, even when the same method is used?
Prices vary depending on the amount of bone required, individual anatomy, the duration of the procedure, and the type of bone graft material used. The surgeon’s experience and the clinic’s infrastructure also play a role. - Does an implant become more expensive if a bone graft is necessary?
Yes. A bone graft is an additional surgical procedure and increases the total cost due to extra materials, operating time, and a longer overall treatment process. - Are there more affordable alternatives to a conventional bone graft?
In some cases, short implants, angled implant placement, or concepts such as All-On-4 can help avoid bone grafting. Whether this is possible depends on the individual jaw anatomy. - Why is bone graft material calculated differently?
Depending on the type of material (synthetic, animal-derived, or autologous bone), billing may be based on weight, unit, or surface area. The size of the granules can also influence the price. - How much does the healing period affect the overall costs?
Longer healing times usually involve additional follow-up visits and delayed implant placement, which can indirectly increase the total treatment costs. - Is bone grafting in the upper jaw more expensive than in the lower jaw?
Often yes, especially if a sinus lift is required. This technique is more complex and typically requires more materials. - Can the costs still change after the operation?
In rare cases, yes—for example, if more bone graft material is needed during surgery than originally planned. - Is it worth comparing bone grafting costs between domestic and international clinics?
Definitely. In countries such as Hungary, surgical and material costs are often significantly lower, while maintaining comparable medical standards.
An important topic is jawbone loss and smoking. Read dental implant with bone grafting testimonials.


